Blockchain know-how has revolutionized the way in which data is saved and transferred, particularly within the realm of cryptocurrencies. The blockchain layer has grow to be a breakthrough innovation of the twenty first century because of its clear and decentralized nature. Nevertheless, understanding the complicated mechanics of blockchain may be troublesome. This text simplifies the complexity by deciphering the varied layers of the blockchain, offering perception into its performance, and exploring its purposes throughout the crypto area.
The Function of the Blockchain Layer in Cryptography
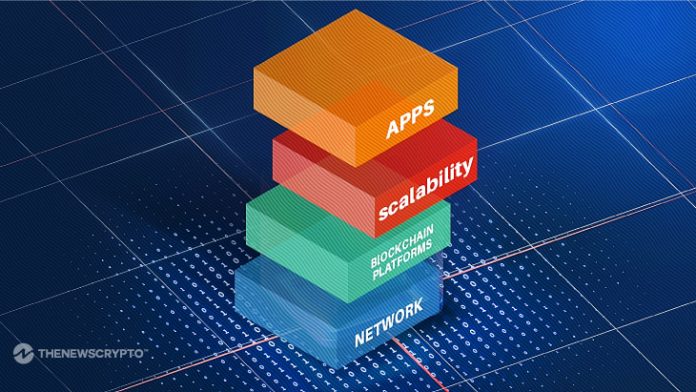
The blockchain layer performs an vital function within the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Layer 0 gives the {hardware} infrastructure, Layer 1 maintains protocols for safe transactions, Layer 2 gives scaling options for quicker and cheaper transactions, and Layer 3 helps DeFi and NFT platforms. It hosts purposes reminiscent of , enabling progressive use instances within the crypto area.
We are going to now focus on the layers of blockchain intimately and clarify how blockchain performs an vital function within the realm of cryptography.
What’s Layer 0 Blockchain?
{Hardware} Layer: Layer 0
On the core of blockchain is the {hardware} infrastructure layer. It consists of a community of computer systems that contribute to the computing energy and safety of the blockchain community. These computer systems, referred to as nodes, decrypt transactions and play an vital function within the verification course of. Layer 0 gives the essential components required for community operation.
What’s Layer 1 Blockchain?
Information Layer: Layer 1
The information layer shops transaction particulars throughout the blockchain. Transactions are recorded in blocks, that are the essential items of the blockchain. Every block incorporates data such because the cryptocurrency despatched, the recipient’s public key, and the sender’s personal key. Blocks are linked to the blocks earlier than and after them to create an immutable chain of transactions.
Layer 1 blockchains reminiscent of Bitcoin and Ethereum function at this layer and preserve the purposeful points of the blockchain community. They act as implementation layers, whose protocols affect the performance of subsequent layers.
What’s Layer 2 Blockchain?
Community Layer: Layer 2
Layer 2 offers with communication between nodes within the blockchain community. Because the blockchain community is an open system, every node should concentrate on the transactions being validated by different nodes. The community layer facilitates this communication, permitting nodes to share and validate transaction data. Layer 2 acts as a scaling resolution, overcoming Layer 1 limitations by way of transaction throughput.
We regularly combine third-party options to reinforce scalability and enhance general community effectivity. Notable Layer 2 applied sciences embody Bitcoin’s Lightning Community and Ethereum’s Polygon.
What’s Layer 3 Blockchain?
Consensus layer: layer 3
The consensus layer performs an vital function in validating blocks throughout the blockchain. This layer ensures that transactions are confirmed and added to the chain with out duplication or manipulation. Consensus mechanisms reminiscent of Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are carried out at Layer 3. In PoW, validators compete to unravel complicated math puzzles, and the primary to unravel wins the best so as to add blocks. blockchain.
PoS, then again, randomly selects validators primarily based on the stake they maintain within the community. Layer 3, also referred to as the applying layer, hosts decentralized purposes (dApps) and protocols that allow varied user-facing purposes throughout the crypto ecosystem.
Key variations between layers 0, 1, 2, and three:
| layer | clarification | distinguished customers | Instance of use |
| Layer 0 | {hardware} infrastructure | cryptocurrency alternate | Computing assets, strong community operations |
| Layer 1 | protocol | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Ripple | safe transactions, knowledge |
| layer 2 | Scaling resolution | Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, Uniswap | Enhance transaction velocity, scale back charges, interoperability |
| Layer 3 | Functions and companies | Kraken, Uniswap, Metamask, Pancake Swap, OpenSea, Aave | Charge discount, interoperability, dApps, DeFi platforms, NFTs, cryptocurrency buying and selling |
FAQ
What are Layer 1 and Layer 2 Blockchain Networks?
Layer 1 blockchain networks like Bitcoin function independently with their very own protocol. Layer 2 networks reminiscent of Lightning Community and Polygon present scalability options by constructing on prime of Layer 1 networks.
Do you will have a layer 3 blockchain?
Builders are at the moment within the early phases of layer 3 blockchain improvement, however face challenges to widespread adoption. One of many main hindrances is the shortage of standardized infrastructure for Layer 3 networks that depend on Layer 2 options and require constant and dependable infrastructure.
What’s the goal of layer 2 blockchain?
Layer 2 blockchains are meant to deal with the scalability limitations of layer 1 blockchains. By constructing on prime of Layer 1 networks, Layer 2 options introduce varied methods to extend transaction velocity, scale back fees, and enhance general community effectivity.
how is LAyer 1 and layer 2 blockchain Interplay?
Layer 2 blockchains leverage Layer 1 safety and introduce distinctive mechanisms for processing transactions and enhancing scalability.
Are layer 2 blockchains extra scalable than layer 1?
Sure, Layer 2 improves scalability by implementing off-chain processing and different optimizations.
finish block notes
Understanding the layers of the blockchain is crucial to understanding the internal workings of cryptocurrencies. Every layer serves its personal goal and contributes to the general performance. Layer 0 gives the essential {hardware} infrastructure, whereas Layer 1 maintains the protocol and runs the blockchain. Layer 2 introduces a scaling resolution to extend transaction velocity and scale back charges. Lastly, Layer 3 hosts purposes and companies reminiscent of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms and non-fungible token (NFT) marketplaces. By leveraging the distinct benefits of every layer, the cryptocurrency neighborhood will proceed to drive innovation and form the way forward for decentralized finance.
(Tag translation) Altcoin






Comments are closed.